In April 2022, IEC 62061 was published in the Official Journal of the EU as harmonised standard EN IEC 62061, the content being identical. As a result, presumption of conformity has officially come into force within the EU. A manufacturer can assume that he meets the health and safety requirements of the Machinery Directive if he complies with the provisions of the EU standard. In the conformity assessment procedure, he can issue the declaration of conformity and so affix the CE mark to his plant or machinery.
Presumption of conformity for the previous version EN 62061:2005 ends on 11 October 2023 at the latest! After this transition period, new declarations of conformity can only be issued on the basis of EN IEC 62061:2021.
The European Commission announced the newly harmonised standards on the EU website with CID 2022/ 621, dated April 2022. As of May 2022, they have not yet been published by the EU Commission in the informal "Summary List"!
Procedure for publishing harmonised standards in the EU
Important changes to IEC 62061 / EN IEC 62061:
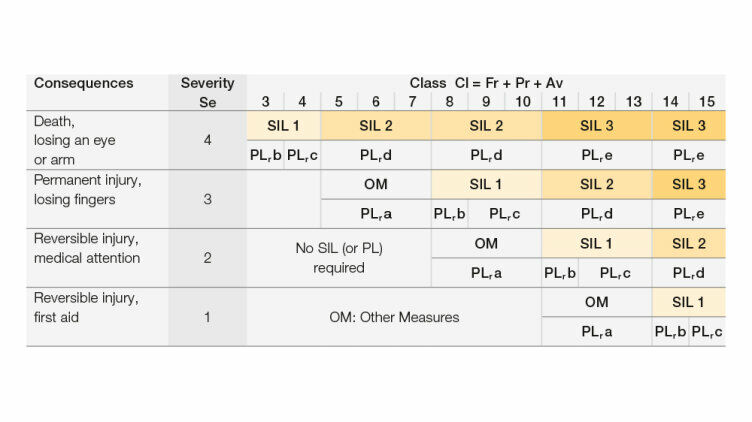
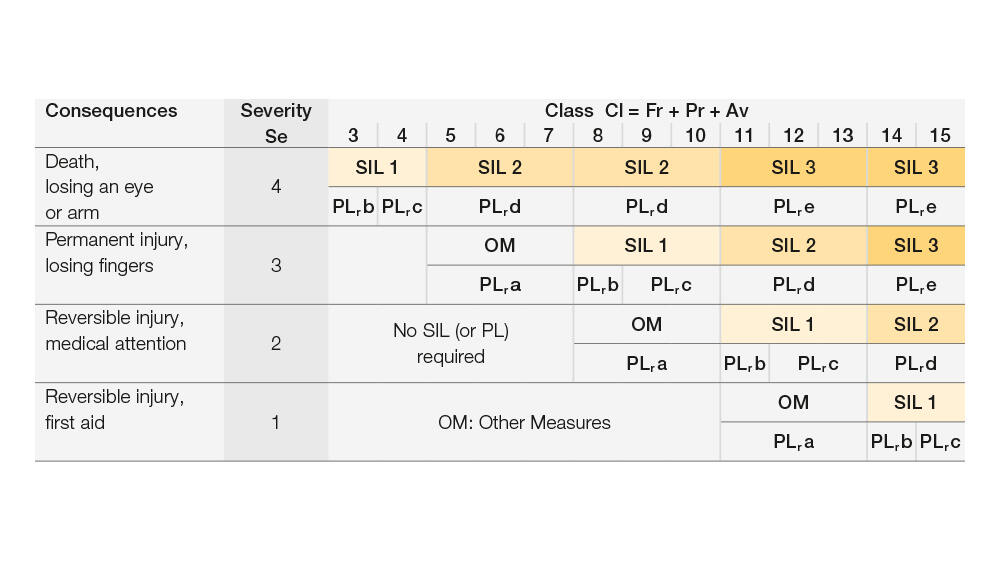
- Changes to the methodology used to define the required SIL level
- The need to draft a Safety Requirements Specification
- The option to use devices developed in accordance with other standards
- More details on safety-related application software