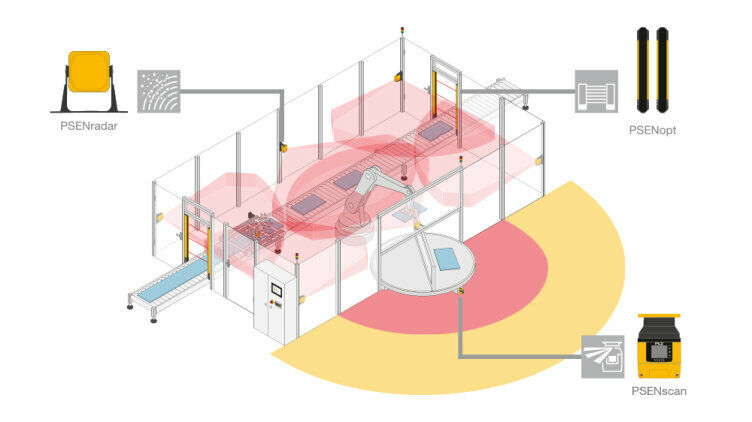
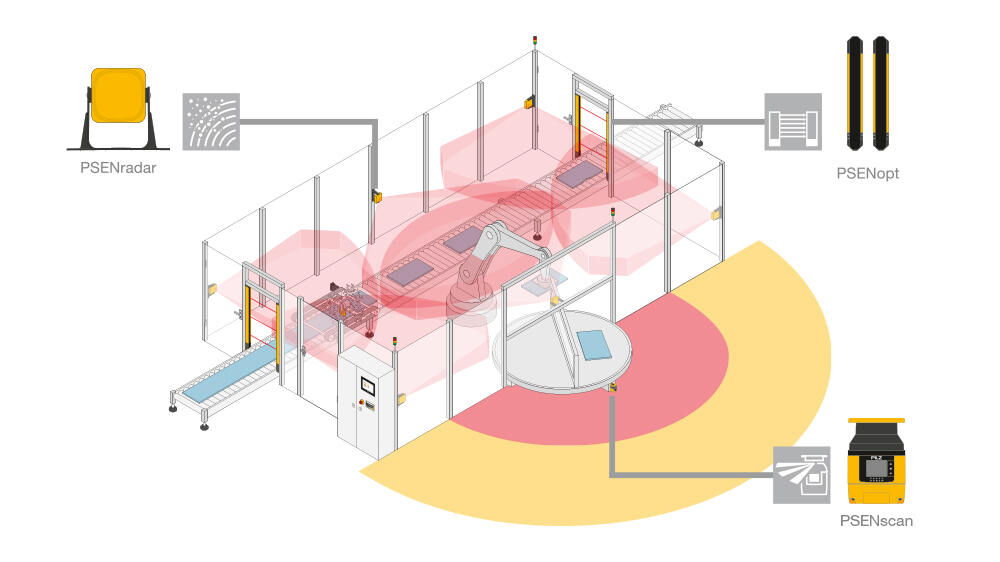
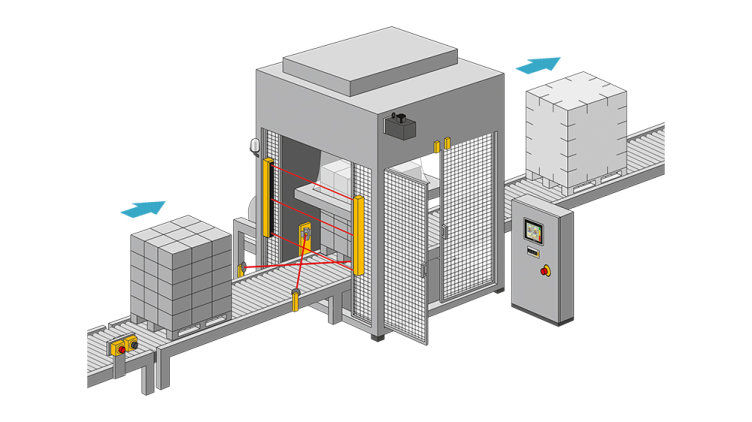
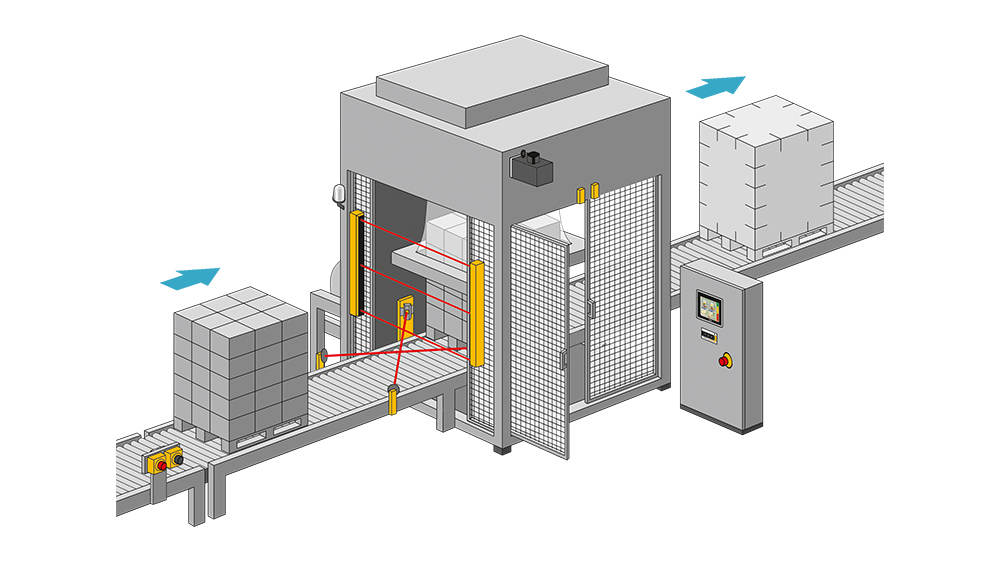
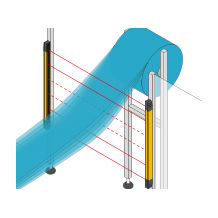
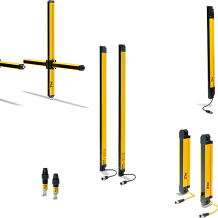
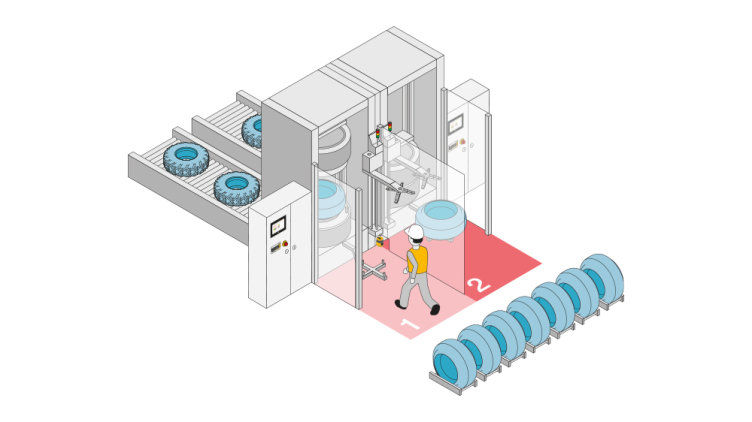
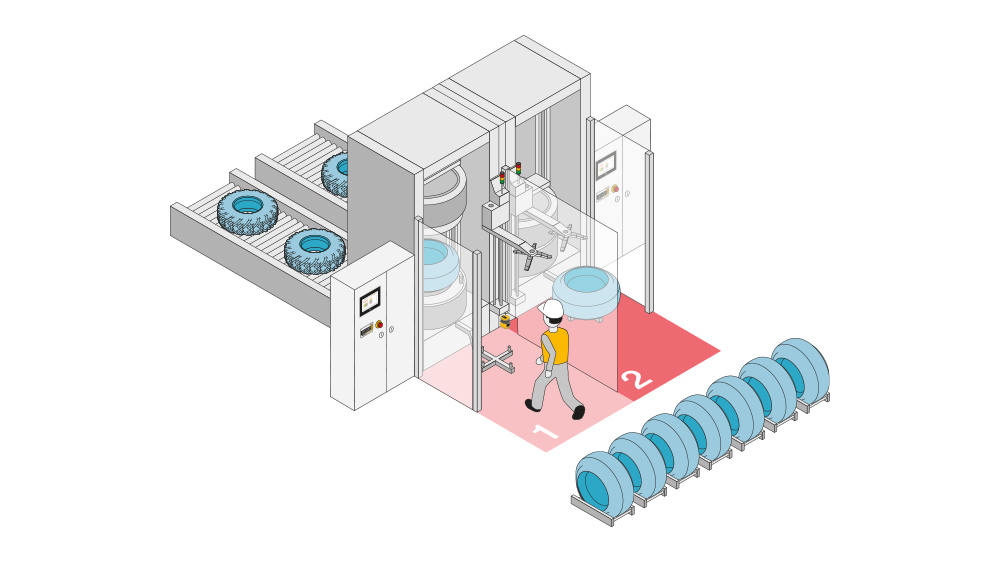
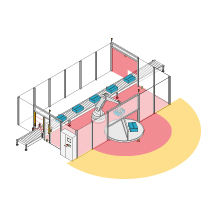
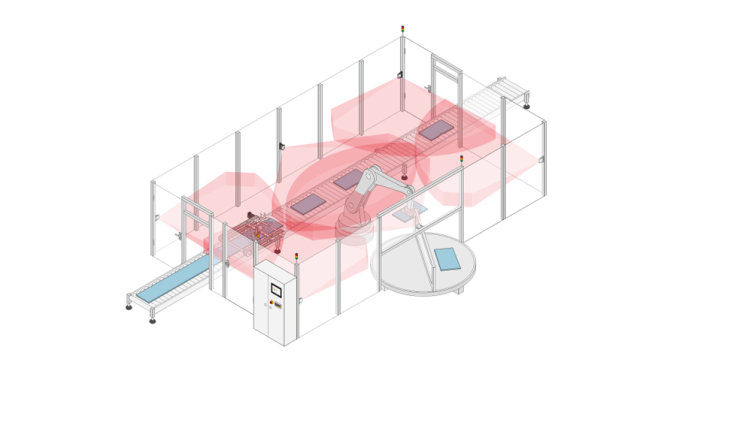
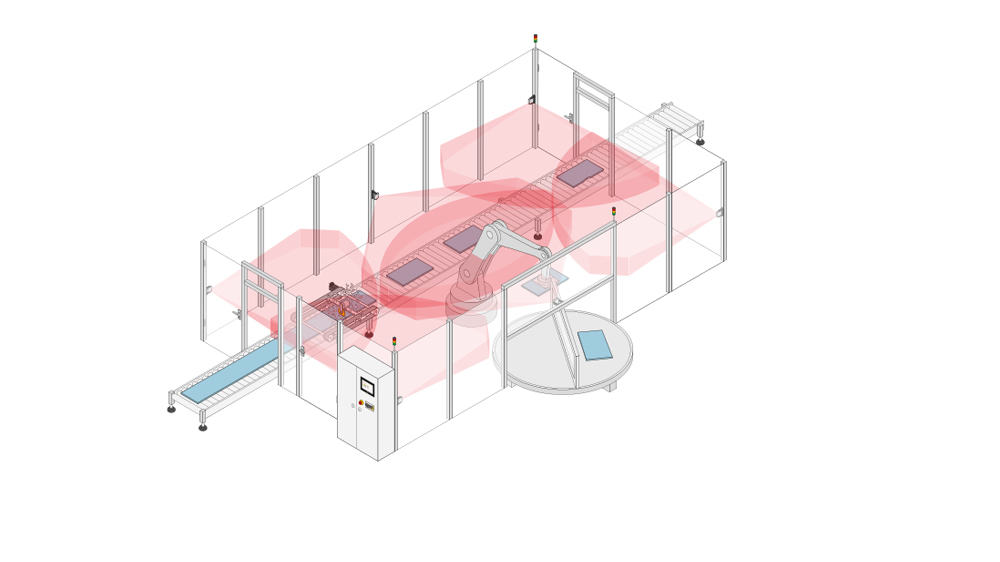
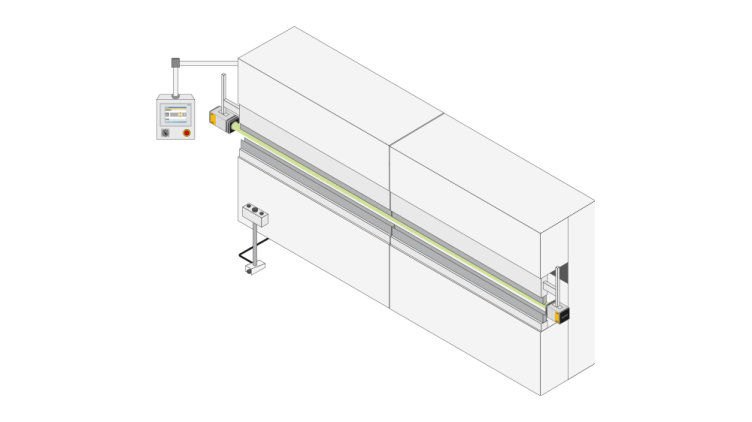
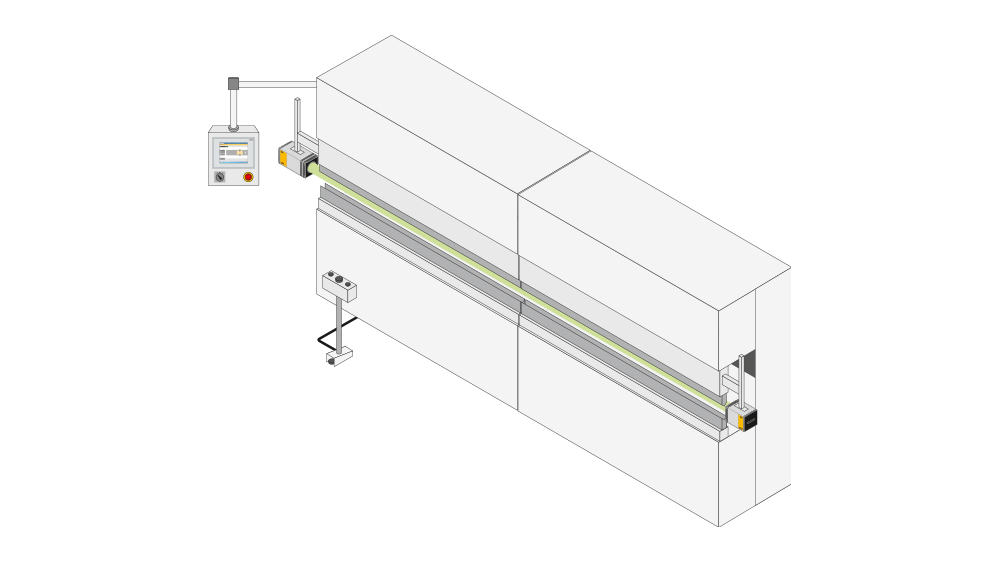
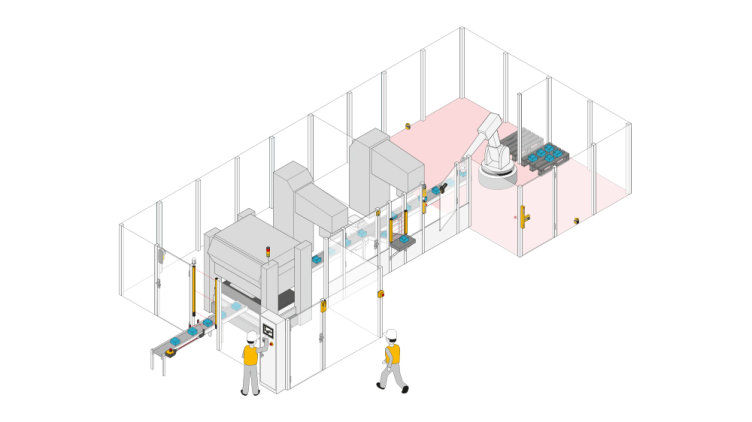
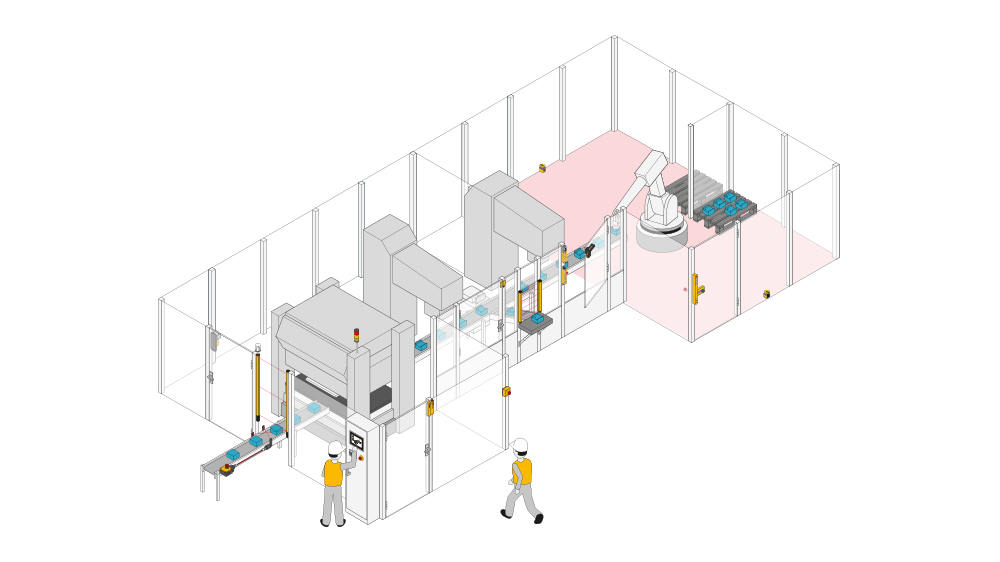
Protective devices particularly include electrosensitive protective equipment (ESPE). This includes the following technologies: optical sensors such as single-beam light barriers and safety light curtains, safety laser scanners and camera-based protection systems. In addition to classic ESPE, secure radar systems also fall under the category of electrosensitive safety solutions.
Common to all technologies: highest safety level, short response times, diagnostic interfaces for troubleshooting, easy configuration and operation, plus robust product features for higher availability. The technologies thus combine safety and productivity with user-friendliness.