Standards are agreements between different interest groups (manufacturers, consumers, notified bodies, health and safety authorities and governments). They describe the state of the art at the time they are produced. Depending on the application site of the machine or product, various statutory regulations may apply, making it necessary to apply various standards. Selecting correctly helps the machine manufacturer to comply with statutory requirements.
Overview of generic standards (A+B standards)
The basis for plant and machinery safety

Generic standards (A and B standards) contain essential information on design, strategy and operation - for the safety of plant and machinery.
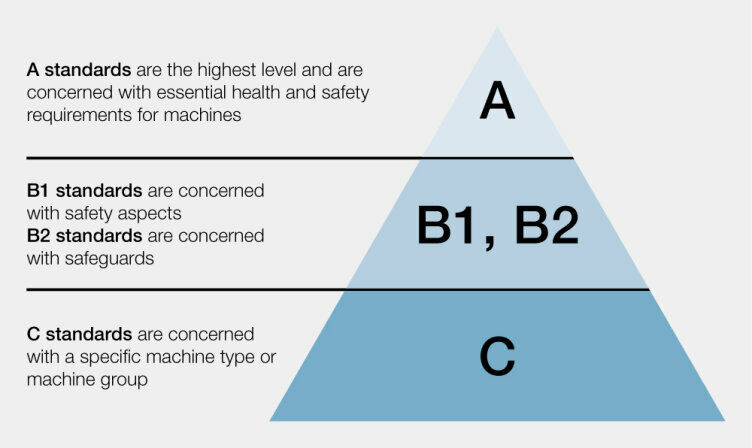
The most important generic standards / A and B standards:
| Risk assessment/risk reduction, functional safety and safety-related requirements | |
|---|---|
| Safety of machinery - General principles for design - Risk assessment and risk reduction | EN ISO 12100 |
| Safety of machinery - Safety-related parts of control systems | EN ISO 13849-1/-2 |
| Safety of machinery - Functional safety of safety-related control systems | IEC 62061 |
| Pneumatic fluid power - General rules and safety requirements for systems and their components | EN ISO 4414 |
| Hydraulic fluid power - General rules and safety requirements for systems and their components | EN ISO 4413 |
| Safety of machinery - Electrical equipment of machines | EN IEC 60204 series |
| Low-voltage switchgear and controlgear | EN IEC 60947-5 series |
|
Selection of safeguards |
|
|---|---|
|
Safety of machinery - Guards - General requirements for the design and construction of fixed and movable guards |
EN ISO 14120 |
|
Safety of machinery - Interlocking devices associated with guards - Principles for design and selection |
EN ISO 14119 |
| Safety of machinery - Prevention of unexpected start-up | EN ISO 14118 |
| Safety of machinery - Electro-sensitive protective equipment (e.g. light grids, light barriers, light curtains, laser scanners, etc.) |
EN IEC 61496-1/-2/-3 |
| Safety of machinery - Pressure sensitive protective devices (e.g. pressure-sensitive safety mats) | EN ISO 13856-1/-2/-3 |
| Safety of machinery - Two-hand control devices - Functional aspects - Principles for design. | EN ISO 13851 |
| Safety of machinery - Emergency stop - Principles for design | EN ISO 13850 |
| Additional protective measures – Safety of machinery | |
|---|---|
| Safety distances (protection of upper/lower limbs) | EN ISO 13857 |
| Minimum gaps to avoid crushing of parts of the human body | EN ISO 13854 |
| Human body measurements, access to machinery, access openings, anthropometric data | EN 547-1/-2/-3 |
| Positioning of safeguards with respect to approach speeds | EN ISO 13855 |
Safeguards are necessary to protect people as much as possible from hazards that may arise during machine operation. It is the duty of the manufacturer to select an appropriate safeguard. This must neither increase the risk nor obstruct work on the machine. It's in the manufacturer's interests to provide precise justification for any decision not to equip certain moving parts with safeguards.
Overview
Pilz Automation Safety L.P.
7150 Commerce Boulevard
Canton, MI 48187
USA
Telephone: +1 734 354-0272
E-Mail: info@pilzusa.com
Telephone: +1 877 745-9872
E-Mail: techsupport-us@pilz.com